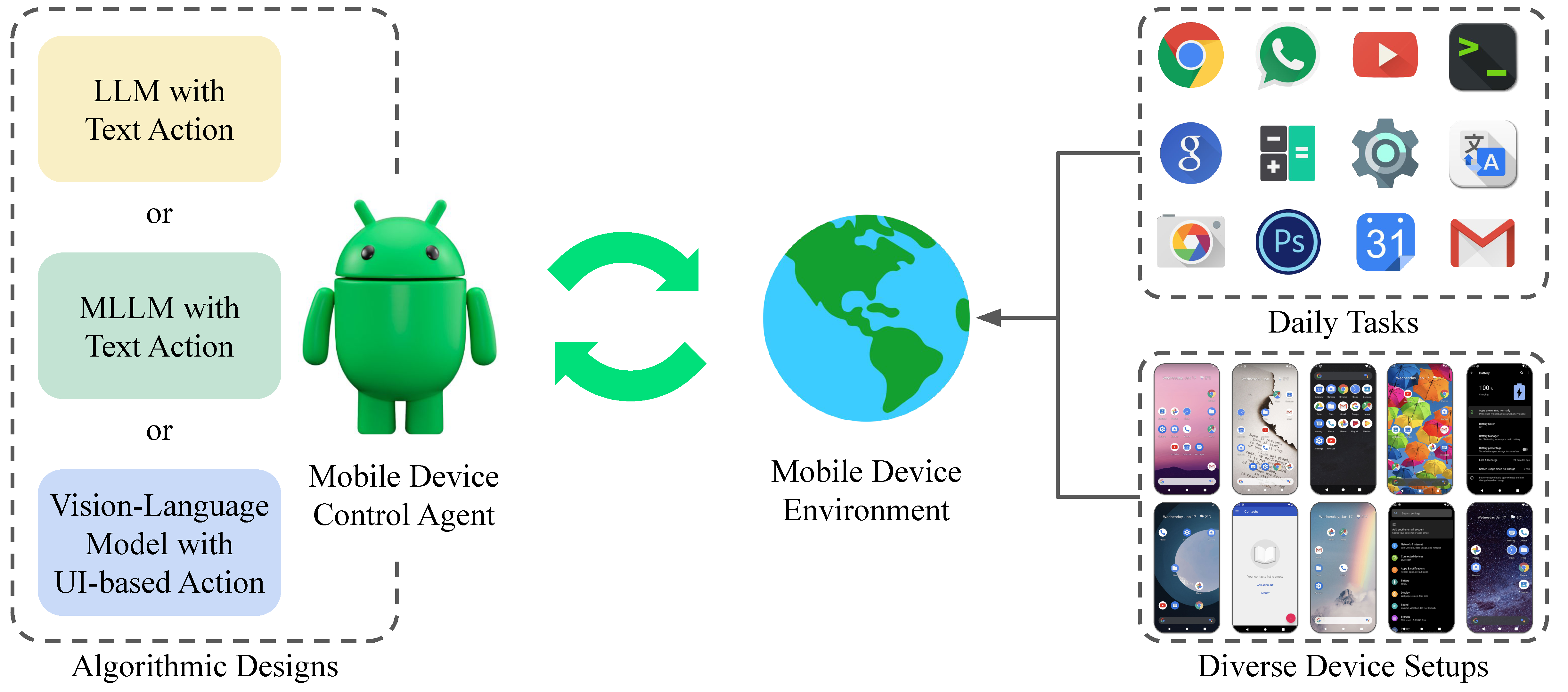
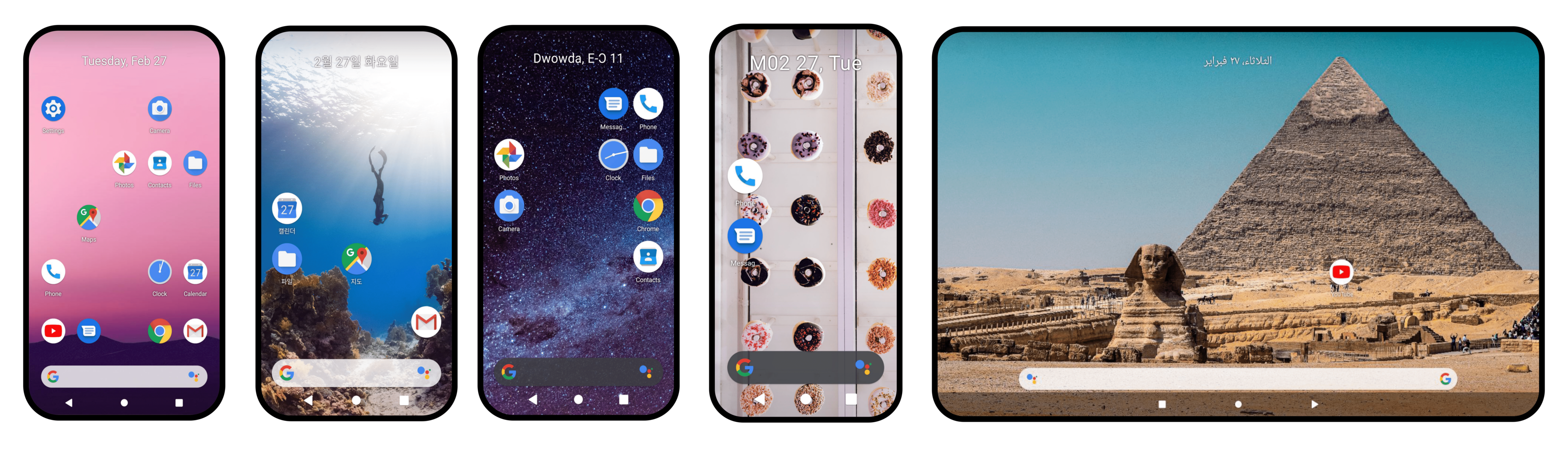
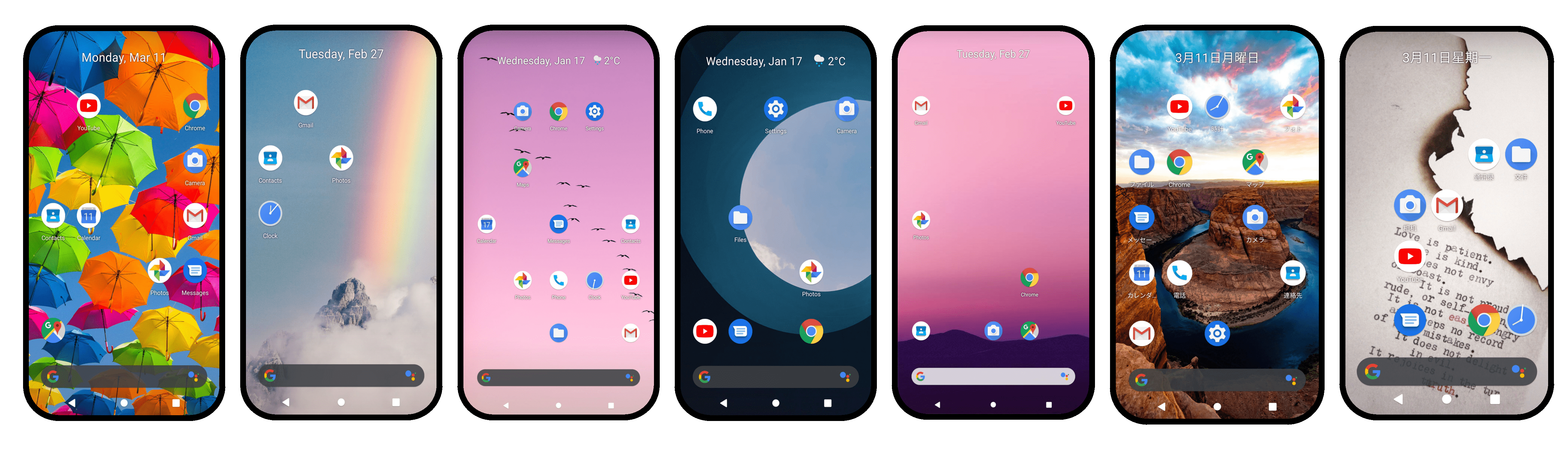
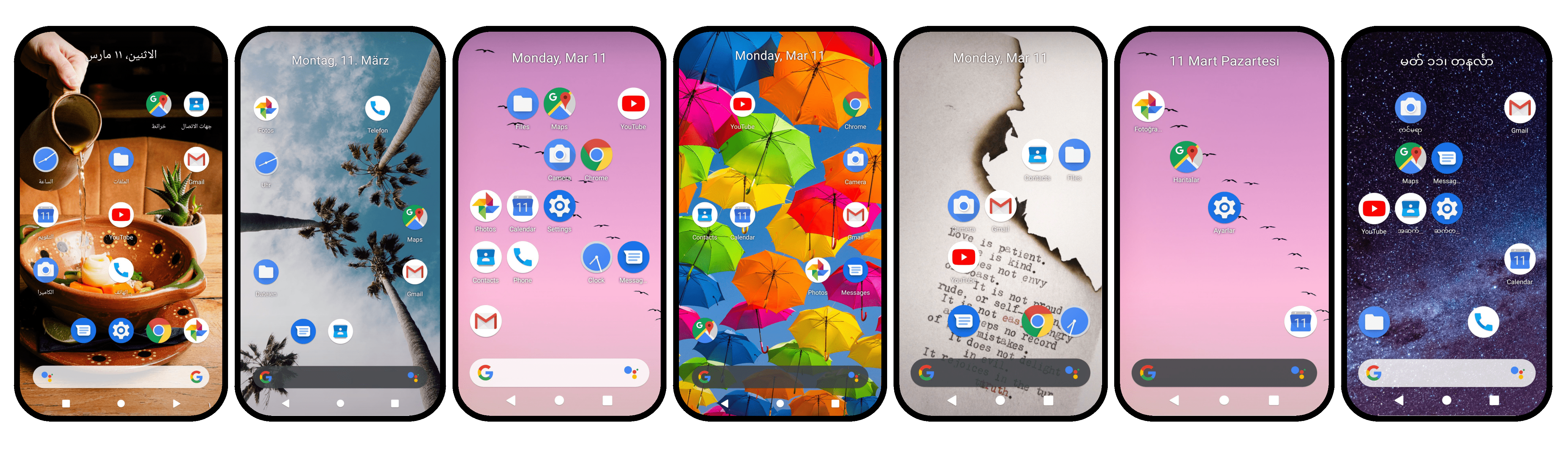
B-MoCA can serve as a testbed for mobile device control agents across diverse device configurations
[Release Notes]
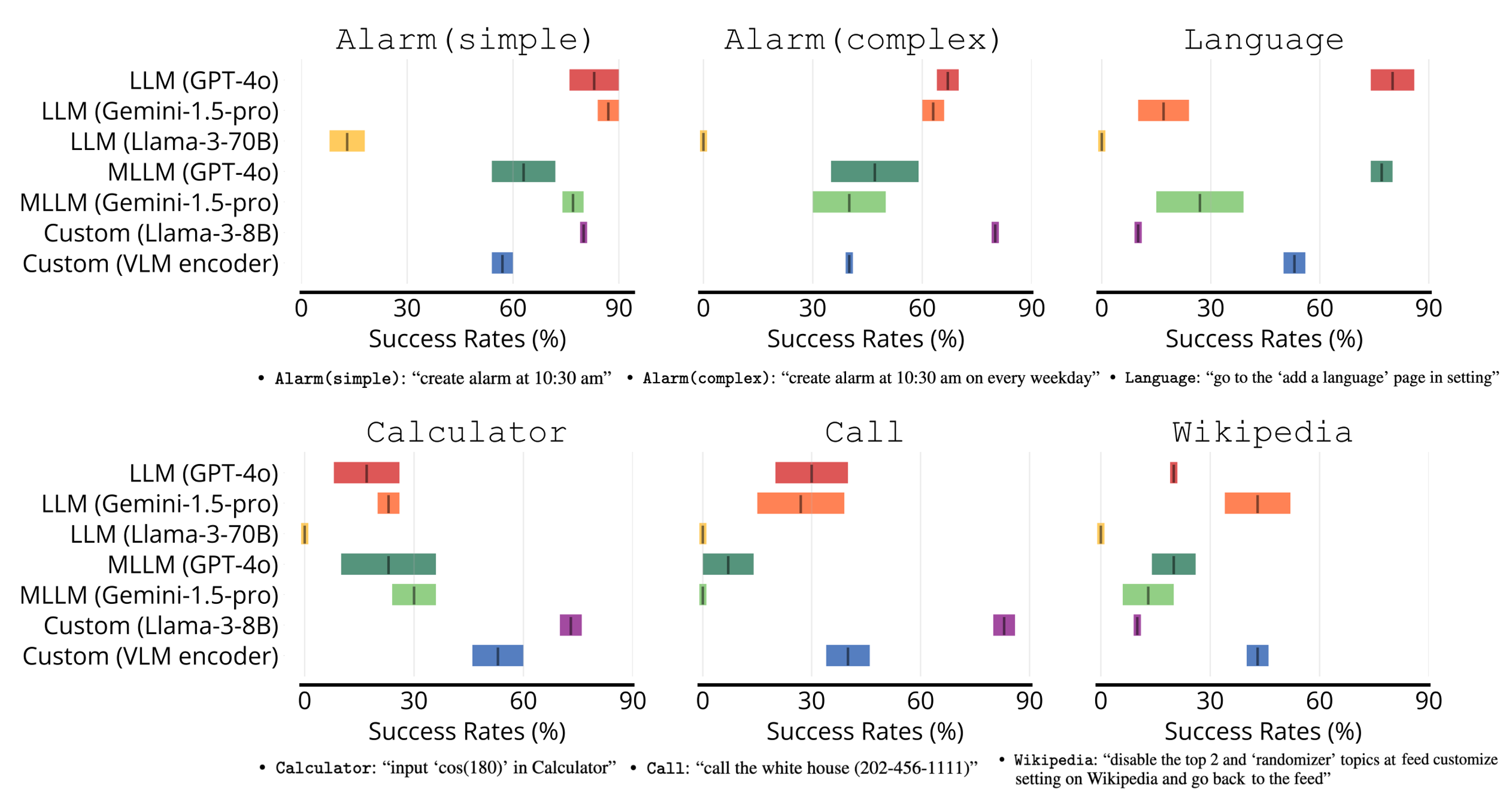
(ver.3) The paper (ver.3) is updated. We updated the action parsing logic, making the performance stabler.(ver.2.5) The paper (ver.2) is updated. We removed 7 tasks (total 131 tasks), due to high stochasticity during evaluation. We show the success rates of representative agents (GPT-4o and Gemini-1.5-pro) on 131 tasks and the success rates of all baseline agents (including custom agents) on six challenging representative tasks.
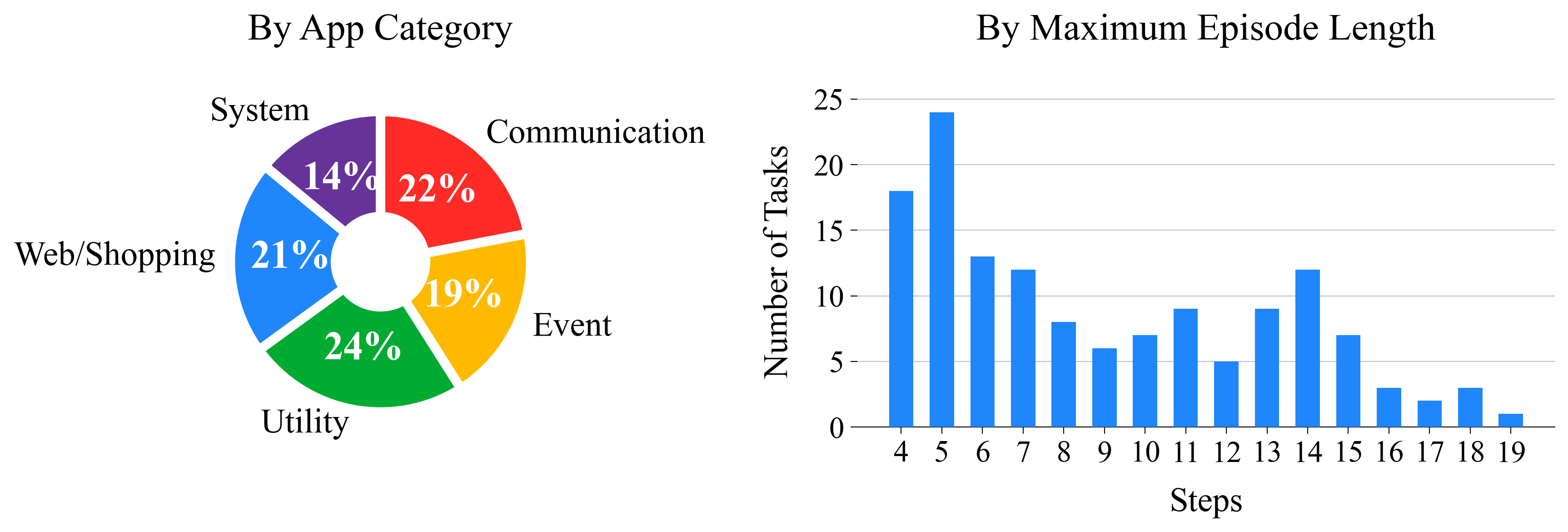
(ver.2.4) We added 39 more daily tasks (total 138 tasks, as removing a task).
(ver.2) We added 30 more daily tasks (total 100 tasks). We updated the observation parsing function (link), which improves the performance of LLM agents by a large margin.
(ver.1) First public release! We presented 70 daily tasks on interactive real Android emulator environments with a randomization feature over the device settings. We conducted an analysis using GPT-4/GPT-4V and Gemini-1.0-pro/Gemini-1.0-pro-V. The paper (ver.1; link) and code (ver.1; link) are available.
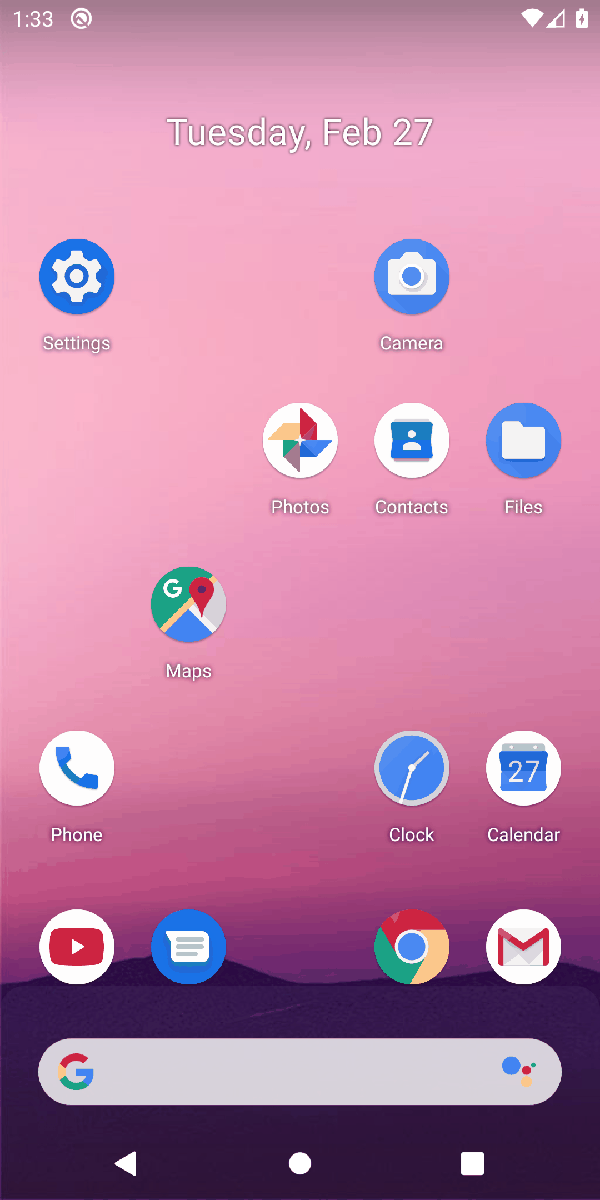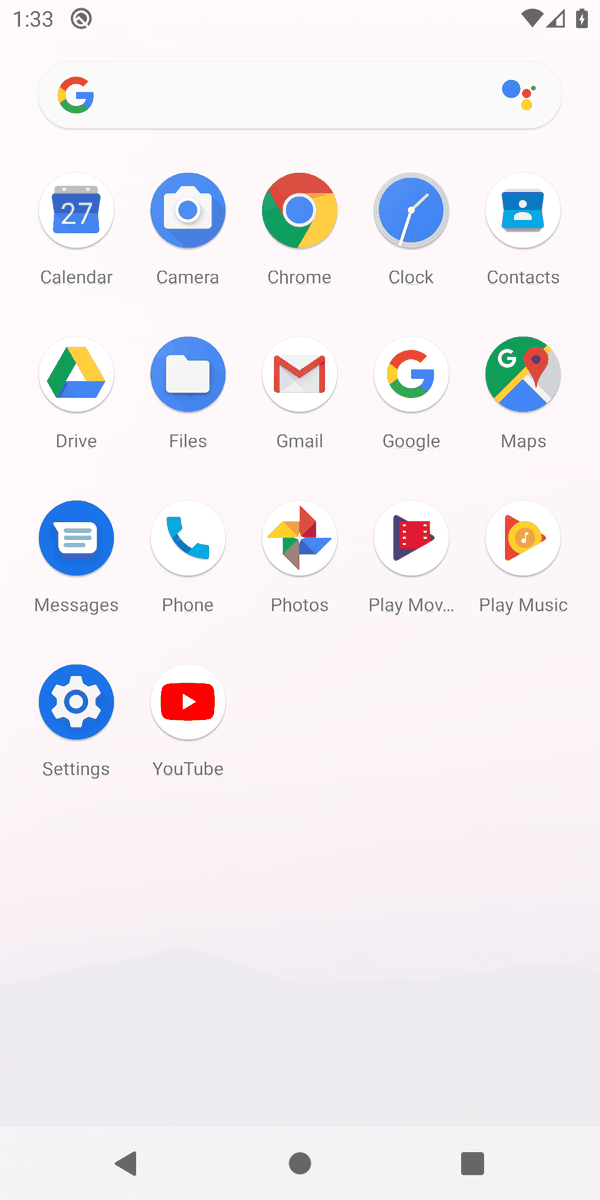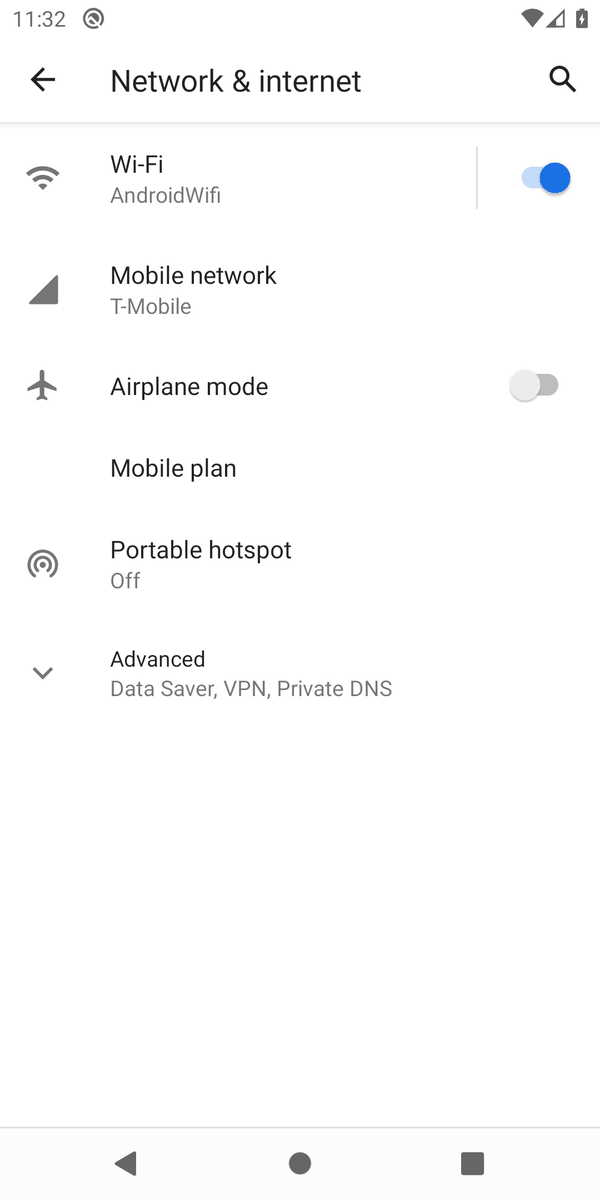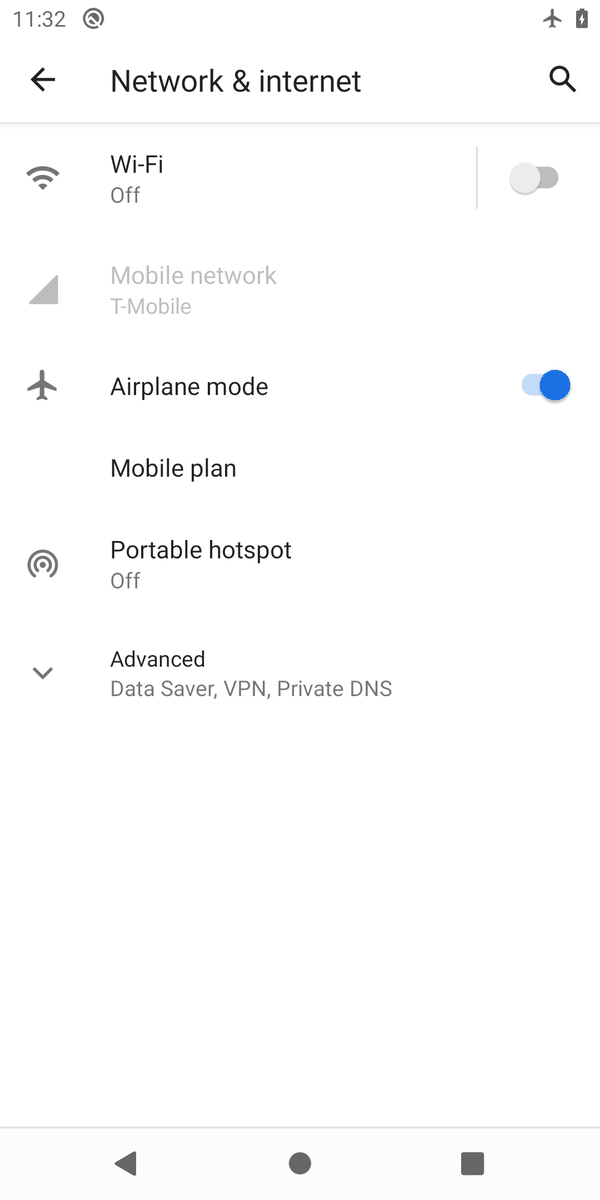
"Turn on the airplane mode"
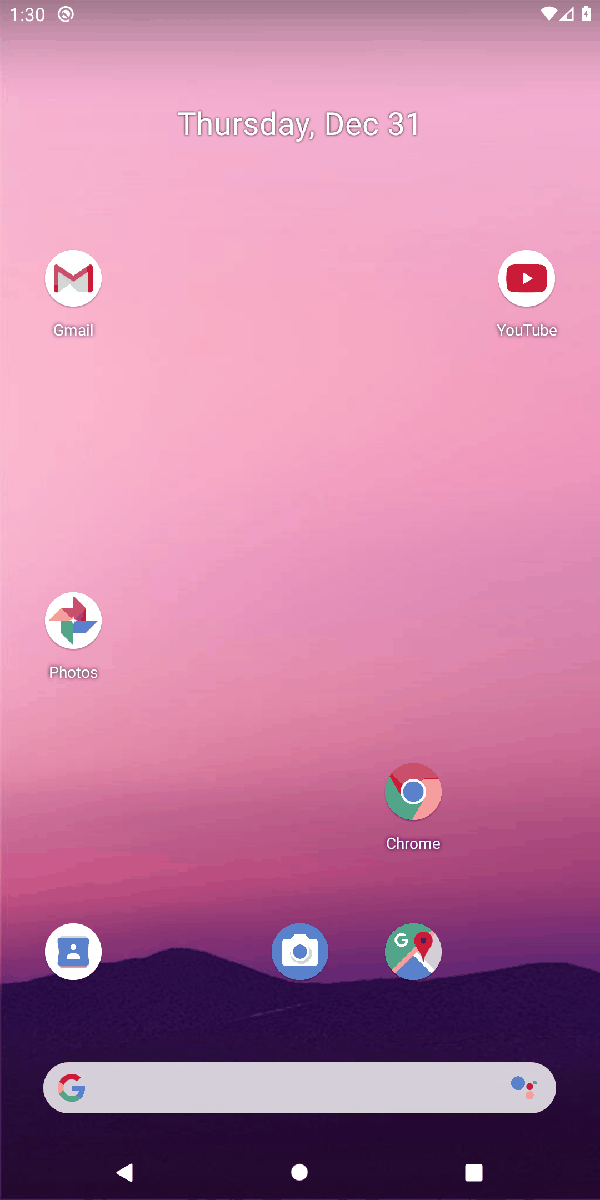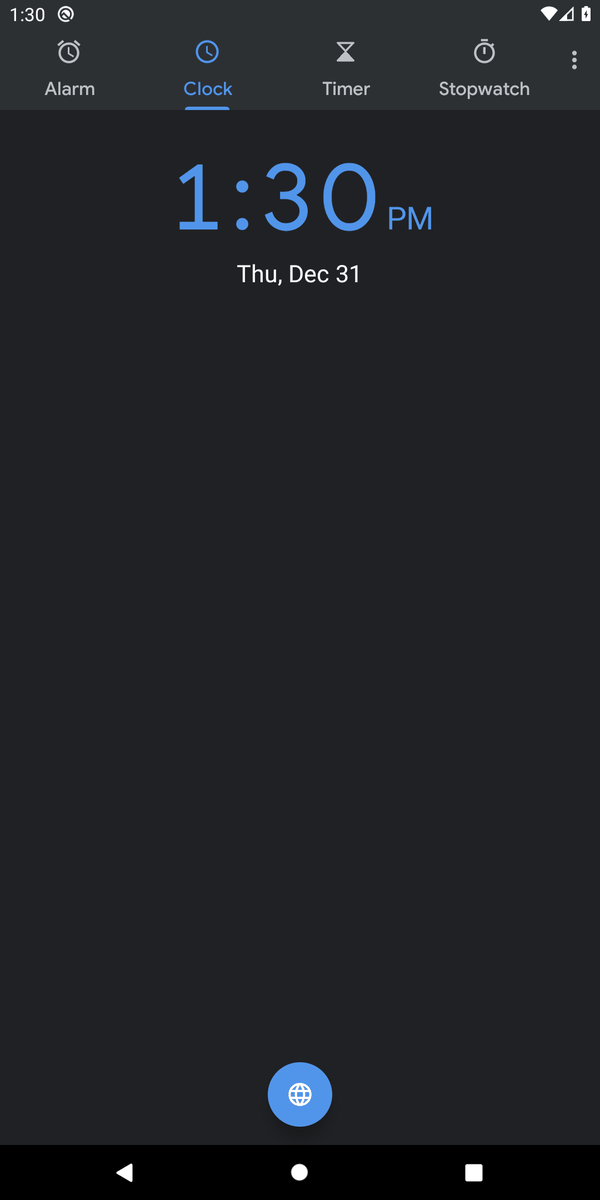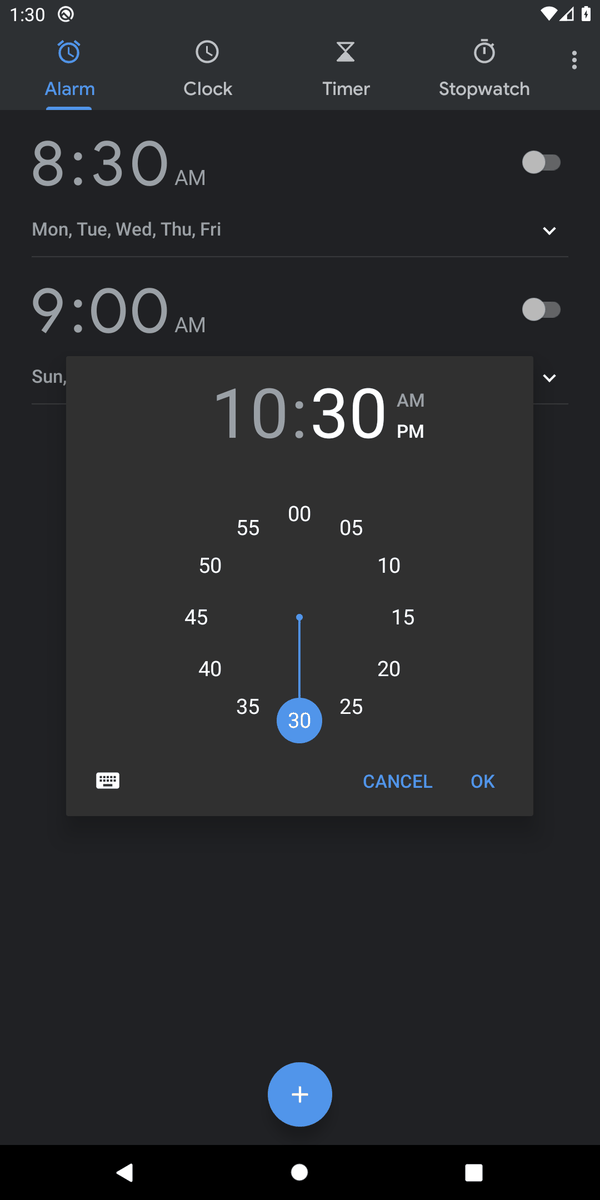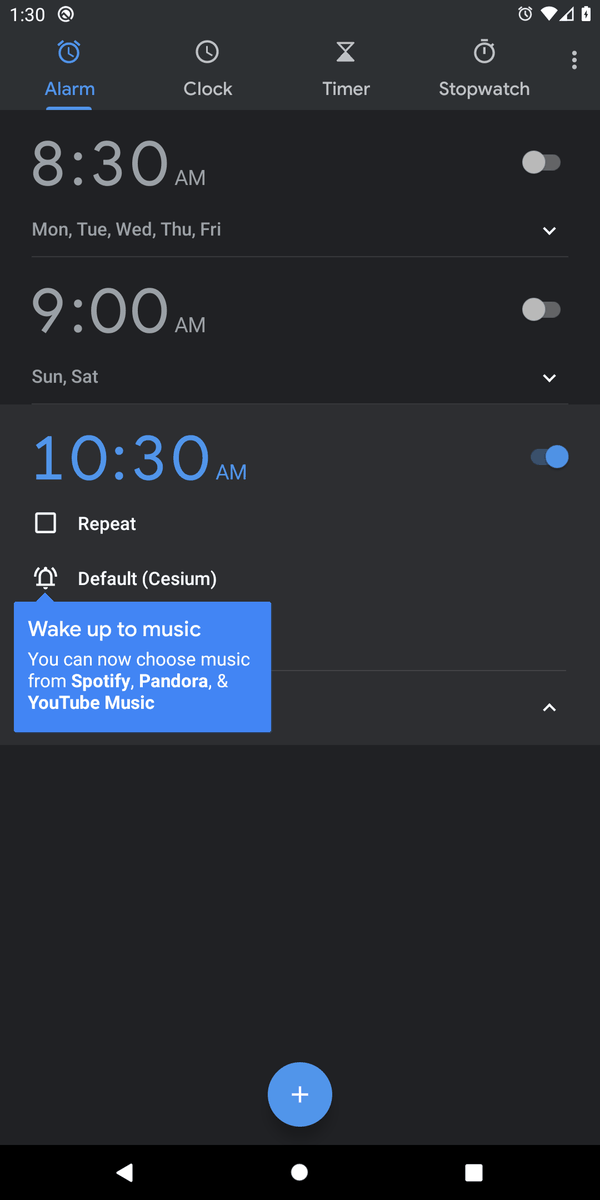
"Create an alarm at 10:30 am"
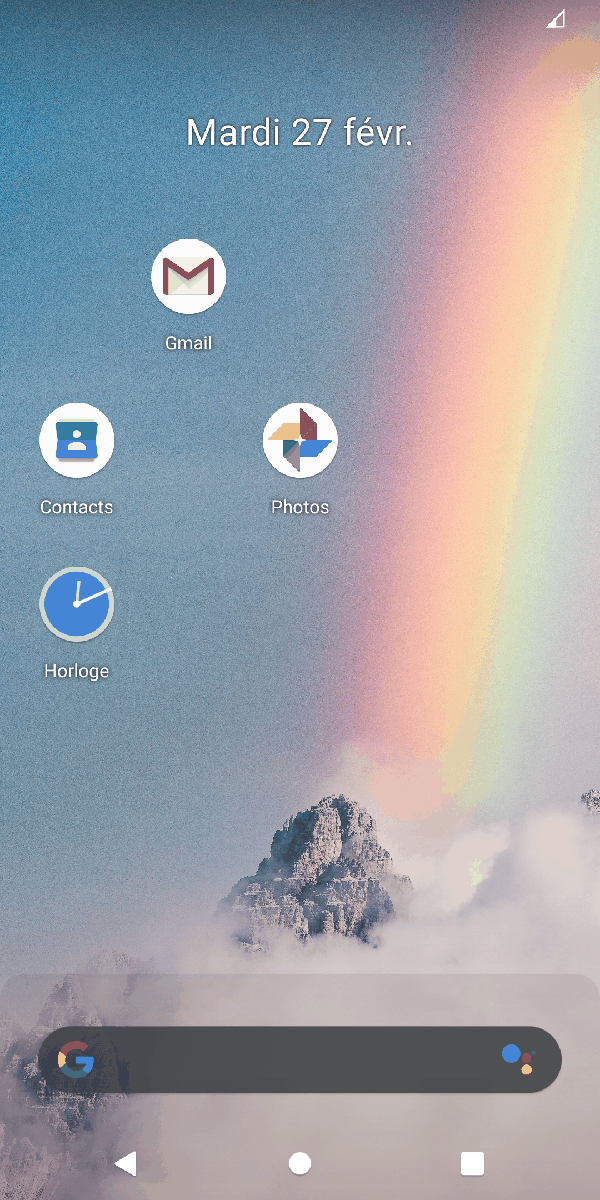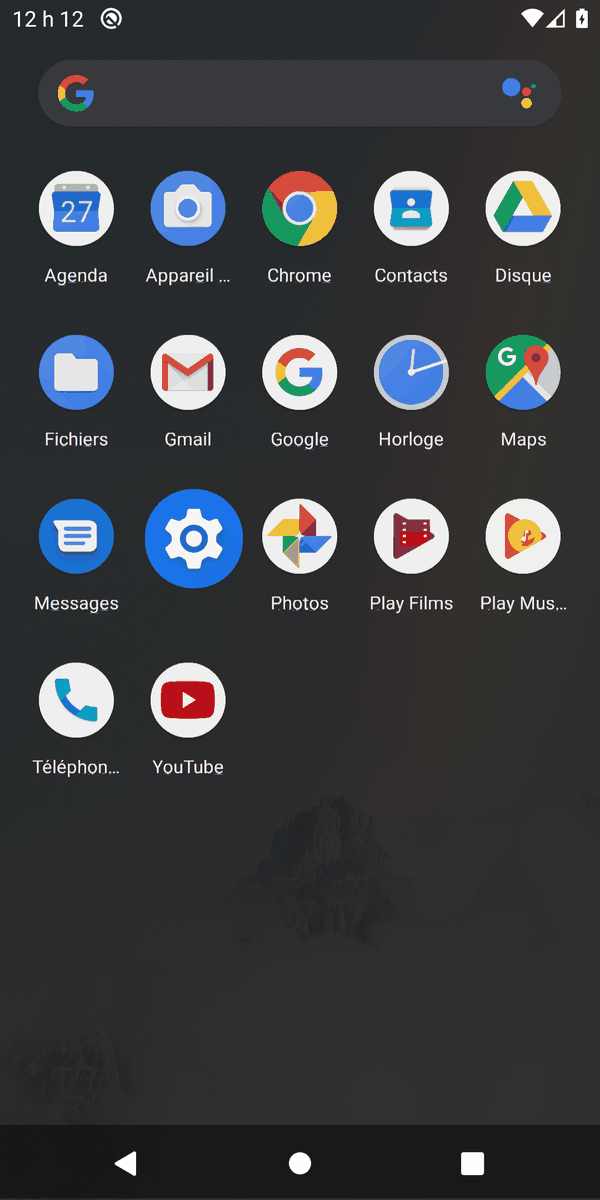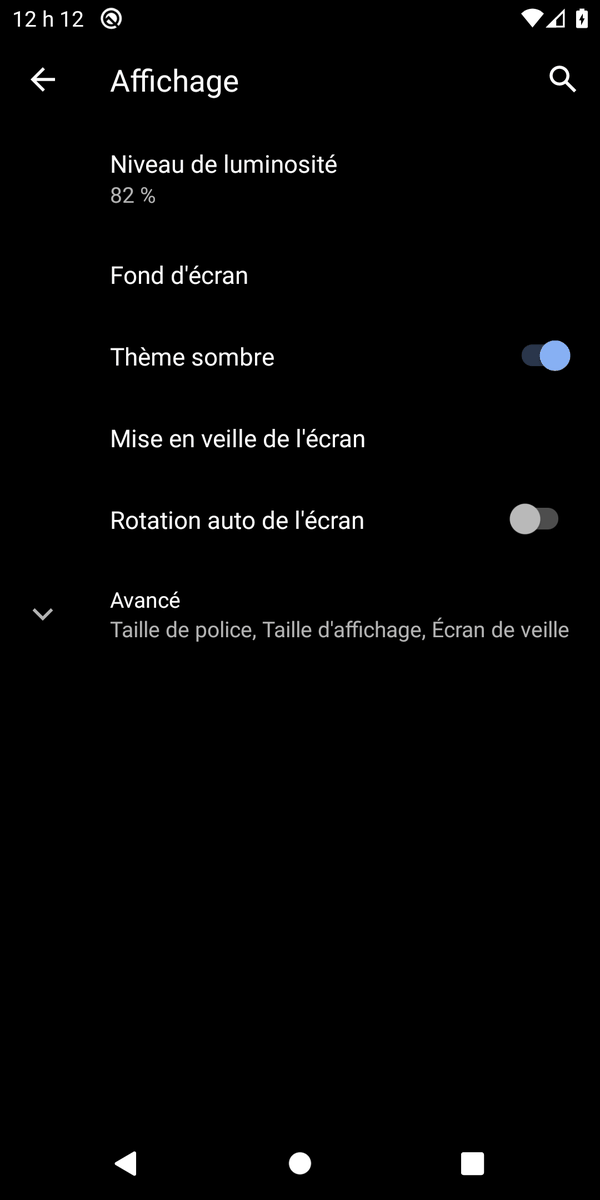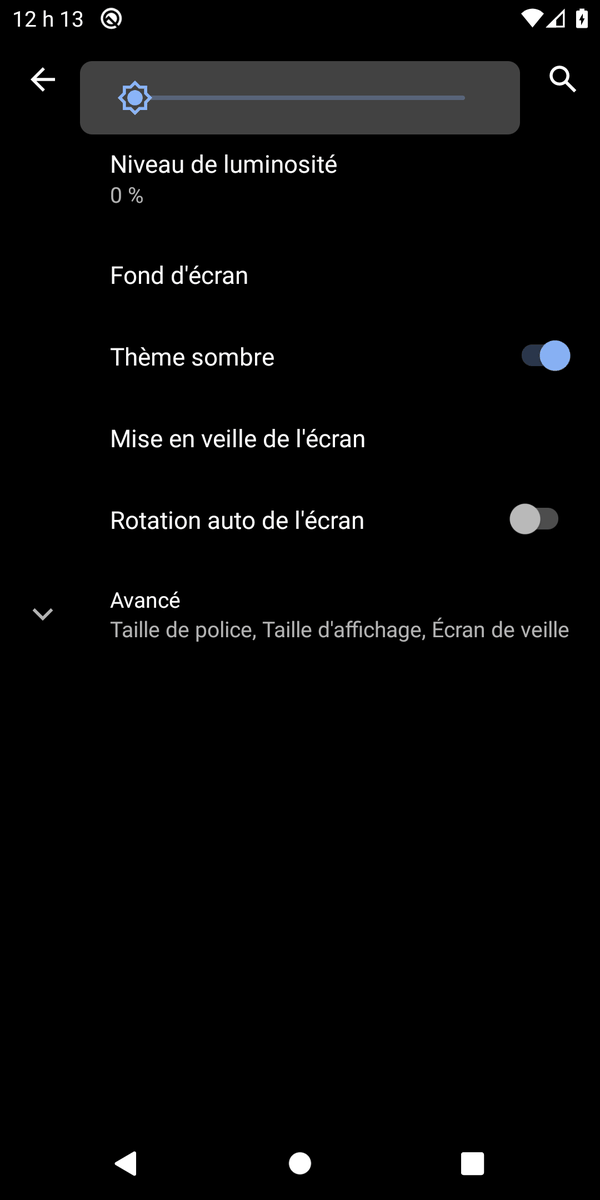
"Decrease the screen brightness"
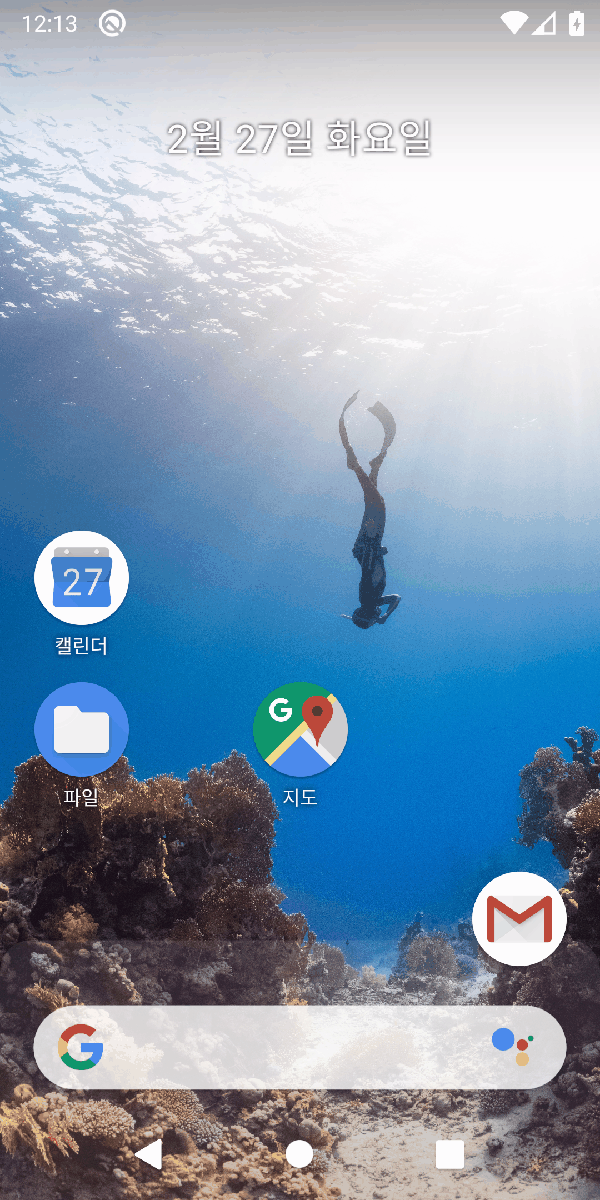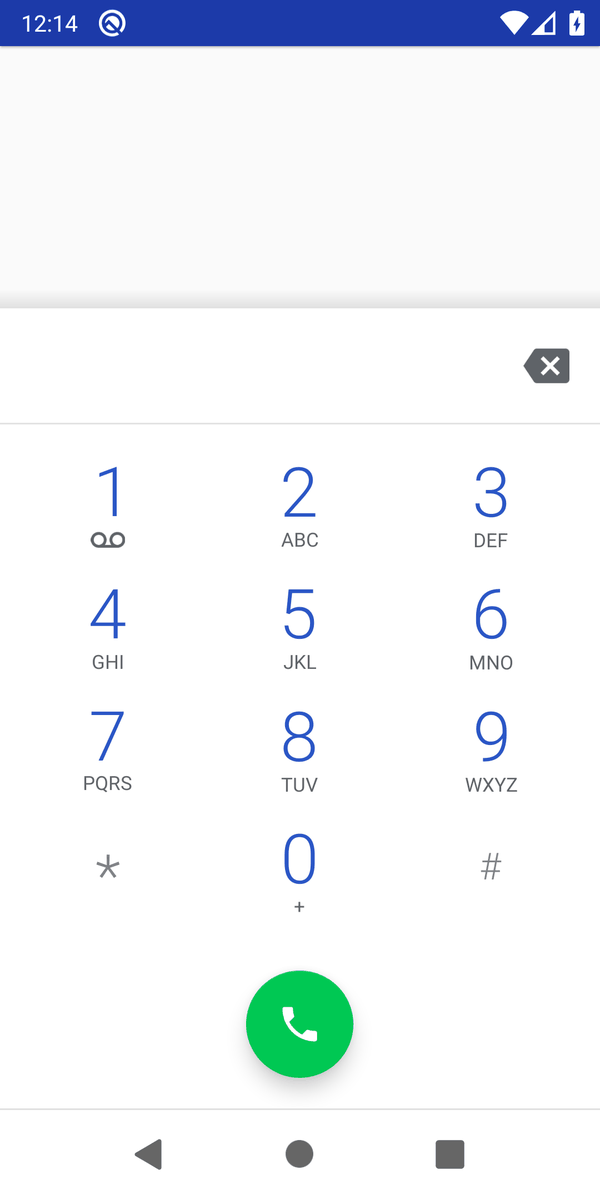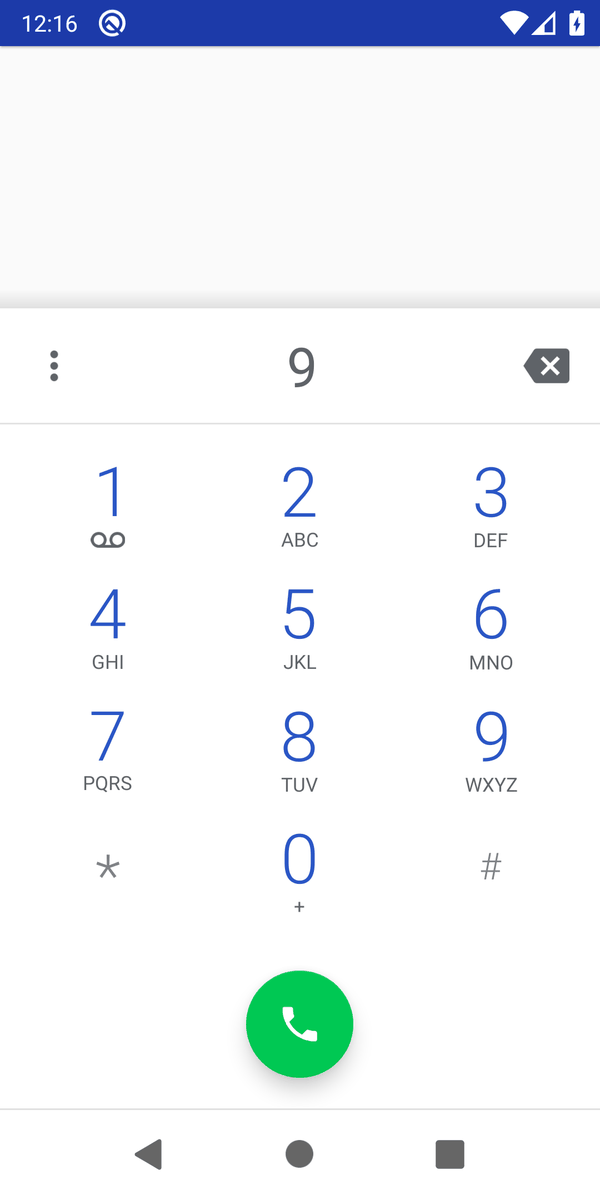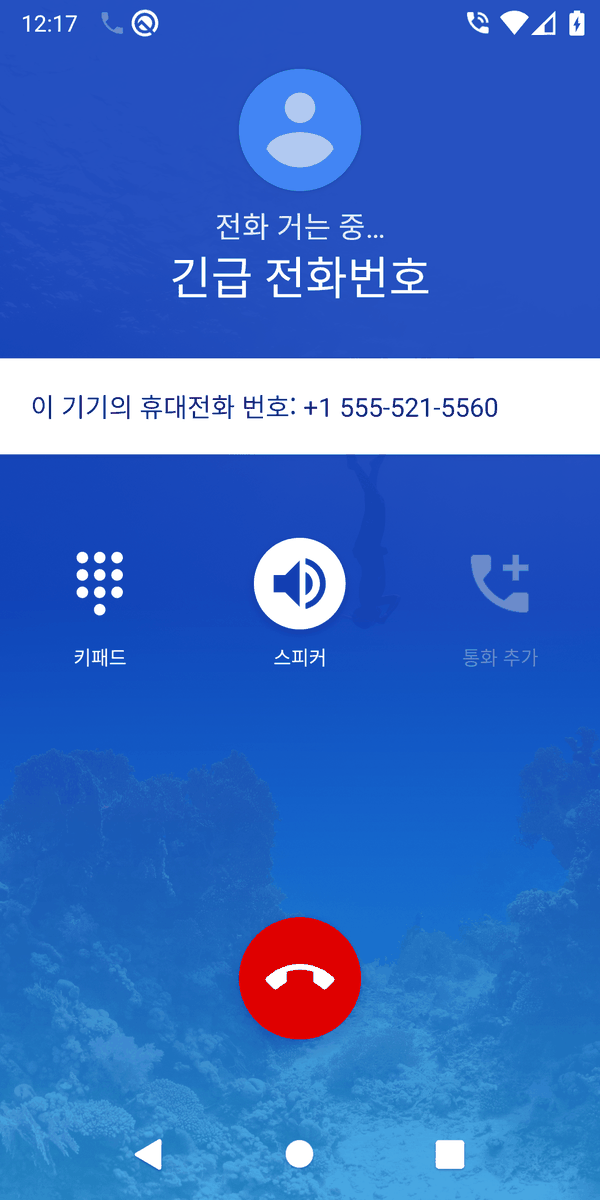
"Call 911"
[Exemplary daily tasks performed by the agents]